Understanding How Fluoride Works
Tooth decay is primarily caused by bacteria that reside in our mouths. These bacteria thrive on leftover food particles, particularly sugary foods and beverages. When they consume sugars, they produce acids that attack tooth enamel. Over time, this acid exposure can lead to significant damage, paving the way for cavities.
Fluoride combats cavities by repairing the damage inflicted by these acids through a process known as remineralization. This process not only helps to restore the enamel but also fortifies it against future acid attacks.
The Importance of Fluoride for Children’s Dental Health
From the moment infants are born, their primary (baby) teeth are already developing in their jaws. Even before these teeth emerge, they benefit from fluoride present in the food and drinks consumed. These early exposures to fluoride strengthen the enamel on baby teeth, enhancing their resistance to cavities—a benefit known as systemic fluoride protection.
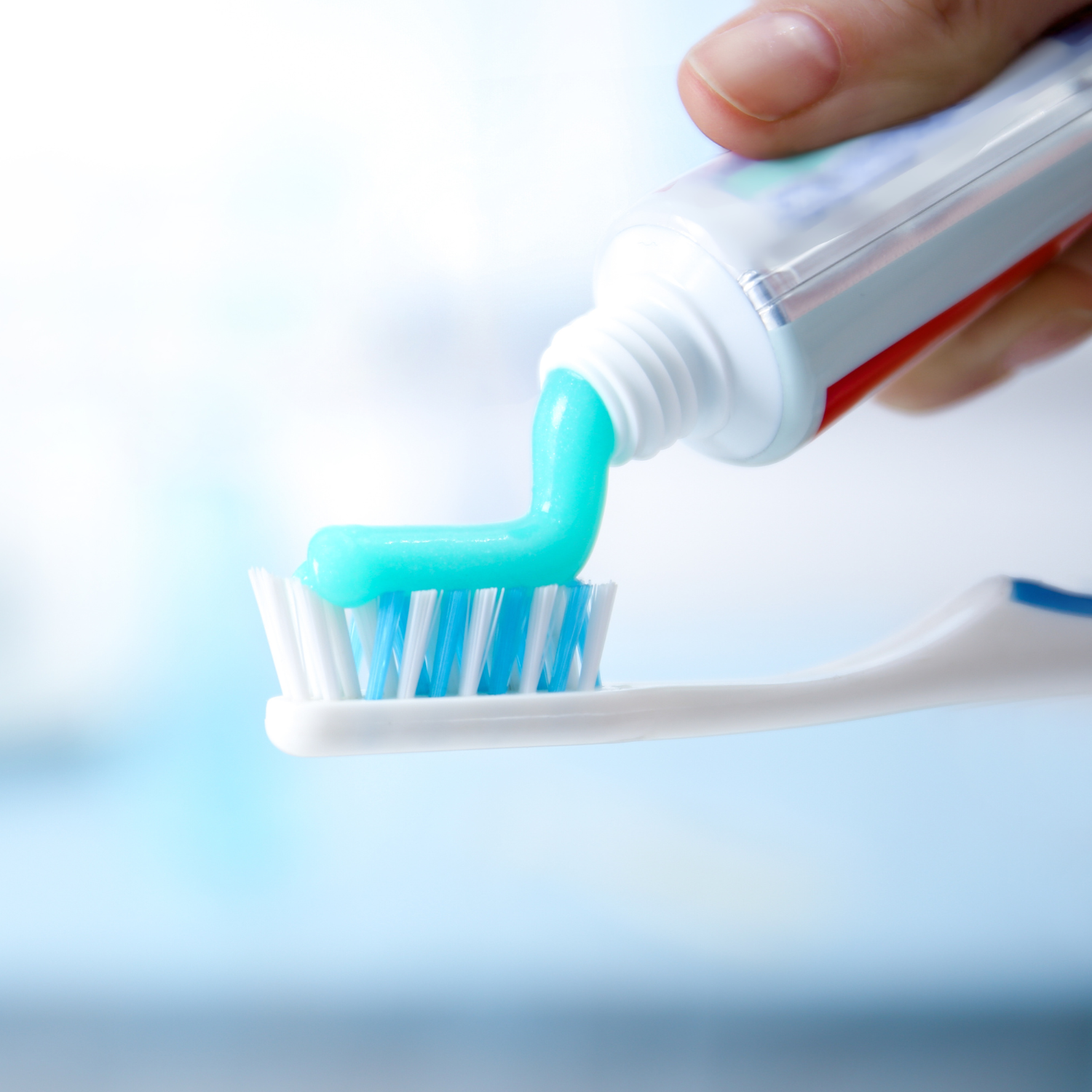
As children’s primary teeth begin to erupt, fluoride continues to play a vital role. It helps repair any damage caused by cavity-causing bacteria that release acids in the mouth. This is why it is essential for children to use fluoride toothpaste and drink fluoridated tap water.
When children use fluoride toothpaste or receive professional fluoride treatments at the dentist, they gain topical benefits. The fluoride applied directly to their teeth creates a protective barrier, while the fluoride from their diet contributes to saliva, which continuously bathes their teeth in small amounts of fluoride, keeping enamel strong and healthy.
The Safety and Effectiveness of Fluoride
For over 70 years, extensive scientific research has demonstrated that adding fluoride to community water supplies is both safe and effective. More than 100 health organizations, including the World Health Organization, the American Medical Association, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the American Dental Association, endorse the cavity-fighting benefits of fluoridated water.
Studies indicate that fluoride in drinking water is particularly beneficial in reducing childhood cavities. For instance, children living in areas without fluoridated water are three times more likely to require dental surgery due to cavities. Furthermore, research shows that fluoride in local water systems can prevent at least 25% of tooth decay across all age groups. Improved dental health not only benefits individuals but also reduces overall healthcare costs, as fewer people require costly cavity treatments.
The Safety and Effectiveness of Fluoride
Fluoride is a natural element found in groundwater and oceans. When fluoride is added to drinking water, it is adjusted to a scientifically recommended level that effectively prevents tooth decay. The current guideline suggests maintaining fluoride levels at 0.7 milligrams per liter of water.
Adding fluoride to water is similar to fortifying certain foods and beverages with vitamins and minerals, ensuring that we receive essential nutrients. Examples include iodine in salt, vitamin D in milk, and calcium in orange juice. Approximately 75% of U.S. water supplies contain added fluoride. You can check if your local water is fluoridated using an online map.
Incorporating Fluoride Toothpaste into Your Dental Routine

Drinking fluoridated water is a vital step in protecting your teeth, but using fluoride toothpaste is equally important. The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends the following brushing tips for all age groups:
- Children under 3 years: As soon as baby teeth appear, gently brush them with a small, soft-bristled toothbrush and a tiny amount of fluoride toothpaste (about the size of a grain of rice).
- Children aged 3 to 6: At this age, children should brush twice daily for at least two minutes each time, using a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste. Supervise them to ensure they use the correct amount and avoid swallowing too much toothpaste.
- Older children and teens: Encourage continued use of fluoride toothpaste in their twice-daily brushing routine. Provide tips for maintaining good oral hygiene.
- Adults: Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste for at least two minutes each time, or as directed by your dentist. Morning and evening brushing is typically recommended.
The Role of Fluoride Mouthwash in Cavity Prevention
Fluoride mouthwash can enhance your teeth’s resistance to decay. If you have concerns about your dental health, consult your dentist to determine if a fluoride mouth rinse is appropriate for you. However, children under age 6 should avoid mouthwash unless recommended by a dentist, as they may be more likely to swallow it.
If you’re looking for fluoride mouthwash or toothpaste, check for products that have earned the ADA Seal of Acceptance.
Professional Fluoride Treatments
During dental visits, your dentist may apply fluoride directly to your teeth. This in-office treatment is often recommended for children to prevent early cavities, but adults can also benefit from fluoride treatments. These treatments may come in the form of gels, foams, or liquids.
In some cases, dentists may prescribe fluoride supplements in the form of tablets, lozenges, or liquid drops for children aged 6 months to 16 years who live in areas without fluoridated water supplies. If you’re concerned that your child or teen isn’t receiving enough fluoride to prevent cavities, consult your dentist, pediatrician, or family physician for guidance.
Fluoride is a powerful tool in the prevention of tooth decay, providing essential benefits for individuals of all ages. By strengthening tooth enamel, promoting remineralization, and reducing acid production, fluoride helps maintain optimal oral health and protects against cavities.
Incorporating fluoride into your daily dental care routine—through drinking water, toothpaste, and professional treatments—can significantly enhance your dental health. For more information on fluoride and to schedule a dental appointment, contact Professional Dental in Utah today. Our dedicated team is here to support your journey toward a healthier, cavity-free smile.